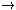 0 since
(v/c)2 is a dimensionless quantity and so this limit will
not depend on the units used to measure the velocity.
0 since
(v/c)2 is a dimensionless quantity and so this limit will
not depend on the units used to measure the velocity.| This is a file in the archives of the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. |
[2.] For a good introduction to the subtleties involved see Sklar, 1967, pp. 118--121.
[3.]
It
is best to think of this limit as (v/c)2
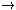 0 since
(v/c)2 is a dimensionless quantity and so this limit will
not depend on the units used to measure the velocity.
0 since
(v/c)2 is a dimensionless quantity and so this limit will
not depend on the units used to measure the velocity.
First published:
Content last modified: